Excel
Because Materialize is PostgreSQL wire-compatible, you can use a standard PostgreSQL ODBC driver to serve data from Materialize into Excel spreadsheets.
Prerequisites
- A Windows machine with Excel.
- Access to your Materialize instance.
- Your Materialize Cloud connection details. For Materialize Cloud, you can find
the connection details from the Materialize Console under
App Passwords -> Connect -> External Tools.
Setup guide
Step 1: Install the Postgres ODBC driver
Install the latest version of the Postgres ODBC driver on your Windows machine from the PostgreSQL ODBC driver download page.
Step 2: Configure ODBC data source
You can set up your ODBC data source via the Windows Control Panel or via a
.reg file.
-
From the Windows control panel, find the
Set up ODBC data sources (64-bit)option (assuming you are using 64-bit version of Excel). -
If you have successfully installed pgODBC, you should see an option in
Create A New Data SourcecalledPostgreSQL Unicode(x64). SelectPostgreSQL Unicode(x64). -
Specify the connection details for Materialize. You can find the details from the Materialize console under
App Passwords -> Connect -> External Tools. ForPassword, use your App Password (which is shown only once during the service account creation).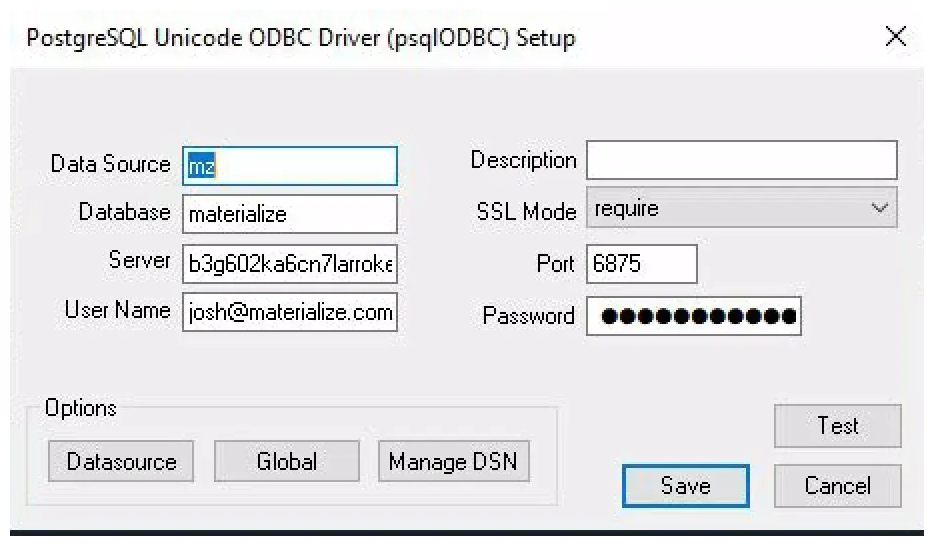
-
If you are using a cluster besides
defaultfor your view, click onDatasourceto get to the Advanced Options. Go toPage 2and addset cluster = <clustername>;in the Connect Settings field. ClickOK.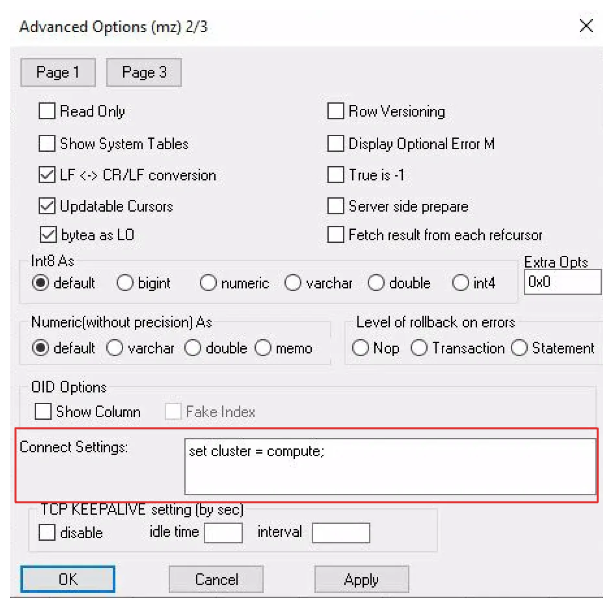
If you are deploying to multiple machines and do not want to use the GUI to
create the ODBC settings, you could instead create a .reg file to deploy the
registry settings. For example, you can save the following sample content as a
.reg file in Windows, updating the:
Driver(path to your psqlODBC installation),Database,Servername,Username,UID,Password, andConnSettings.
-
Passwords stored in
.regfiles are saved in plain text. Restrict access to the file. -
This example creates a User DSN. To create a System DSN, use HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE instead.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\ODBC\ODBC.INI\mz]
"Driver"="C:\\Program Files\\psqlODBC\\1700\\bin\\psqlodbcw.dll"
"CommLog"="2"
"Debug"="2"
"Fetch"="100"
"UniqueIndex"="0"
"UseDeclareFetch"="0"
"UnknownSizes"="0"
"TextAsLongVarchar"="0"
"UnknownsAsLongVarchar"="0"
"BoolsAsChar"="1"
"Parse"="0"
"MaxVarcharSize"="255"
"MaxLongVarcharSize"="8190"
"ExtraSysTablePrefixes"=""
"Description"=""
"Database"="materialize"
"Servername"="your.materialize.server.name"
"Port"="6875"
"Username"="user@materialize.com"
"UID"="user@materialize.com"
"Password"="my_app_password"
"ConnSettings"="set cluster = default;"
"ReadOnly"="0"
"ShowOidColumn"="0"
"FakeOidIndex"="0"
"RowVersioning"="0"
"ShowSystemTables"="0"
"Protocol"=""
"pqopt"=""
"UpdatableCursors"="1"
"LFConversion"="1"
"TrueIsMinus1"="0"
"BI"="0"
"AB"="0"
"ByteaAsLongVarBinary"="1"
"UseServerSidePrepare"="0"
"LowerCaseIdentifier"="0"
"GssAuthUseGSS"="0"
"SSLmode"="require"
"KeepaliveTime"="-1"
"KeepaliveInterval"="-1"
"XaOpt"="1"
"D6"="-101"
"OptionalErrors"="0"
"BatchSize"="100"
"IgnoreTimeout"="0"
"FetchRefcursors"="0"
Step 3: Connect to Materialize from Excel
-
Open Excel. From the Data toolbar, click on
Get Data -> From Other Sources -> From ODBC. -
Select the Data source name created for Materialize and click
OK: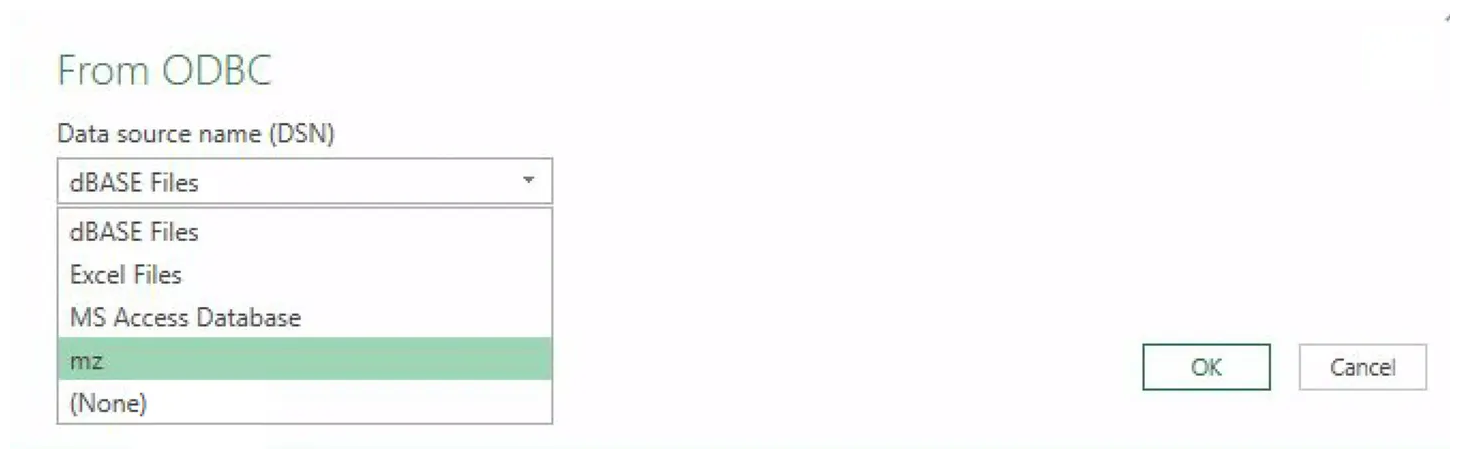
-
Select the
Default or Customtab, then clickConnect. The Navigator pane will open. -
Use the Navigator to select the view whose data you want to load into Excel. Click
Load.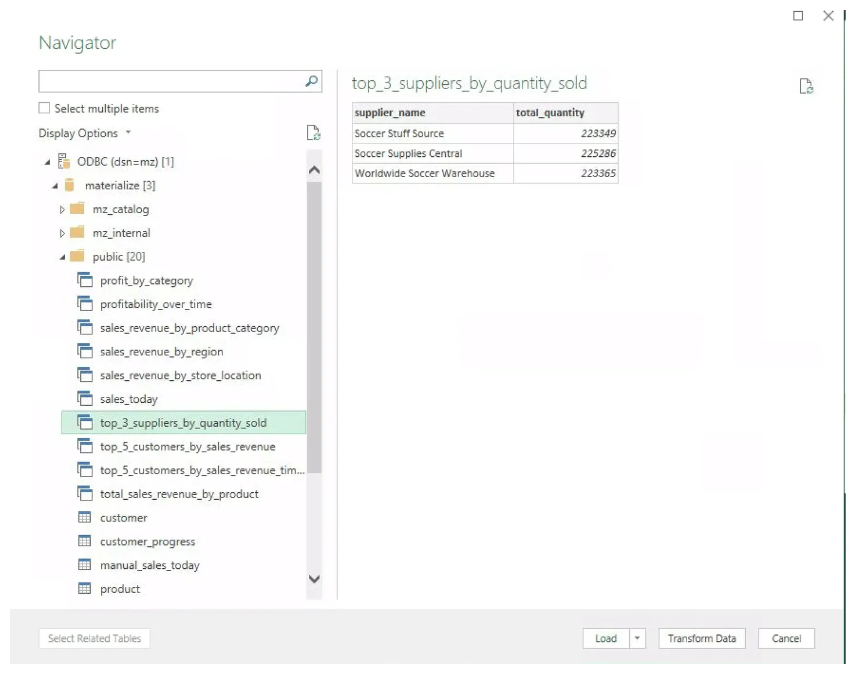
You should see the data in your Excel spreadsheet.
-
Optional. You can manually click on
Data -> Refresh Allto refresh the data.
Step 4: Configure automatic refresh
To refresh as frequently as once per minute, you can update the refresh configuration:
-
Open Query Properties panel. Go to
Data -> Queries & Connections. Right click on a specific query and selectProperties.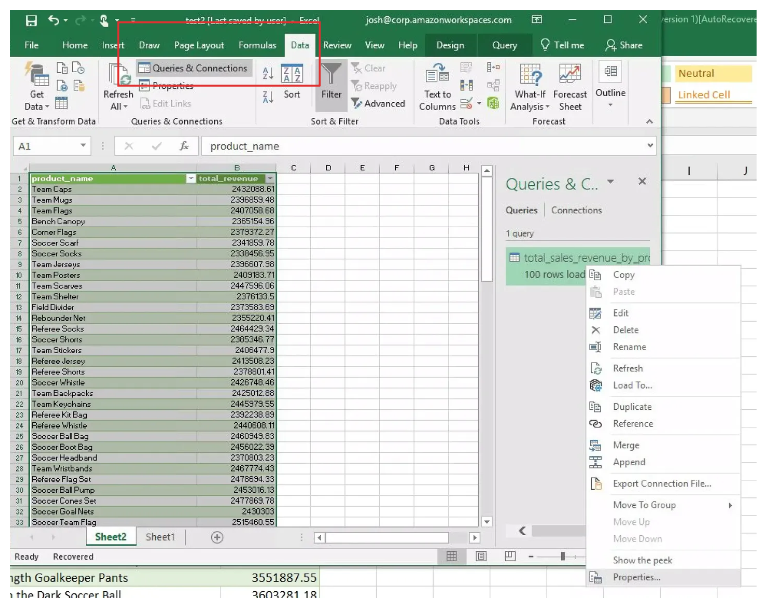 .
. -
Check
Refresh every _ minutesand set the frequency and clickOK.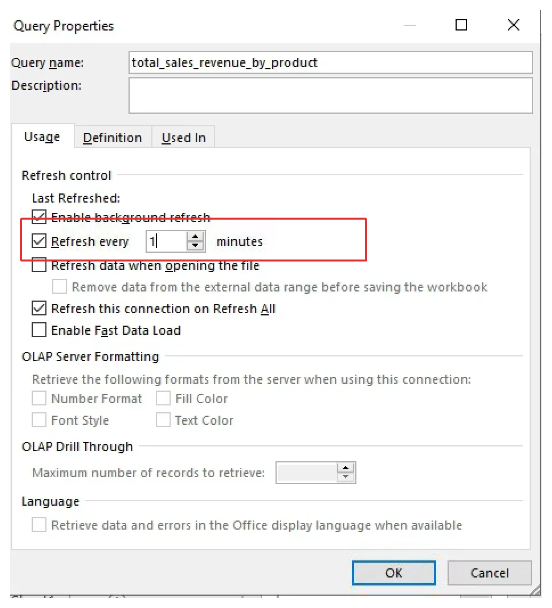 .
.
To refresh more frequently than once per minute requires a custom VBA script. See Custom refresh rate below.
Custom refresh rate
For most scenarios, refreshing every minute is sufficient. However, if you need to refresh more frequently for your use case, you can use a custom VBA script:
-
Press
Alt-F11to open the VBA editor. On the left side, navigate to the VBAProject for your open spreadsheet. -
Right click on
Microsoft Excel Objectsand selectInsert -> Module.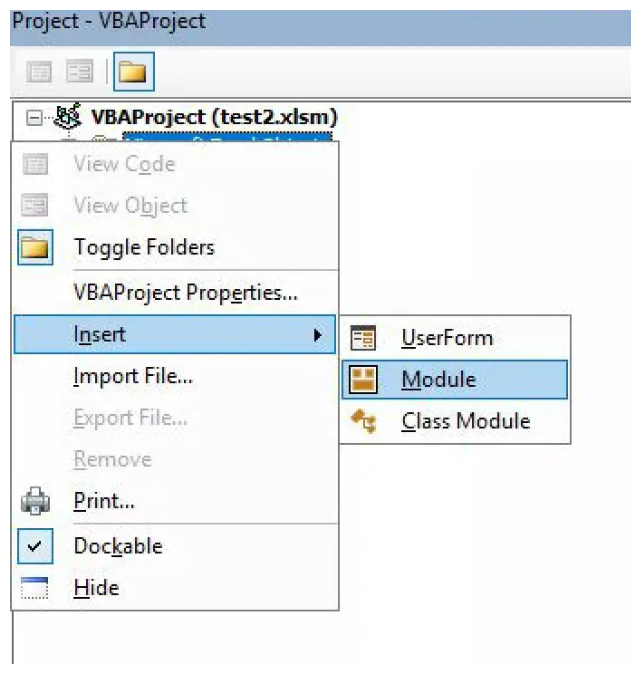 .
. -
In the module editor, copy and paste the following code. Edit the
RefreshPeriodandApplication.OnTimevalues for different refresh rates as required.NOTE: When configuring your refresh interval, note that Excel will throw an error if a refresh does not complete before the next one begins. Depending on your machine, this is typically between 5 and 15 seconds.Sub AutoRefresh() ' Set the data connection to refresh every 15 seconds Dim conn As WorkbookConnection For Each conn In ThisWorkbook.Connections With conn.OLEDBConnection .BackgroundQuery = True .RefreshPeriod = 0.25 ' The property takes minutes as input. 0.25 minutes is equivalent to 15 seconds. .Refresh End With Next conn ' Set the macro to run itself again in 15 seconds Application.OnTime Now + TimeValue("00:00:15"), "AutoRefresh" End Sub -
Press
Alt-Qto close the VBA editor and return to Excel. -
From Excel, you can use
Alt-F8to open up the Macro window and run theAutoRefreshmacro.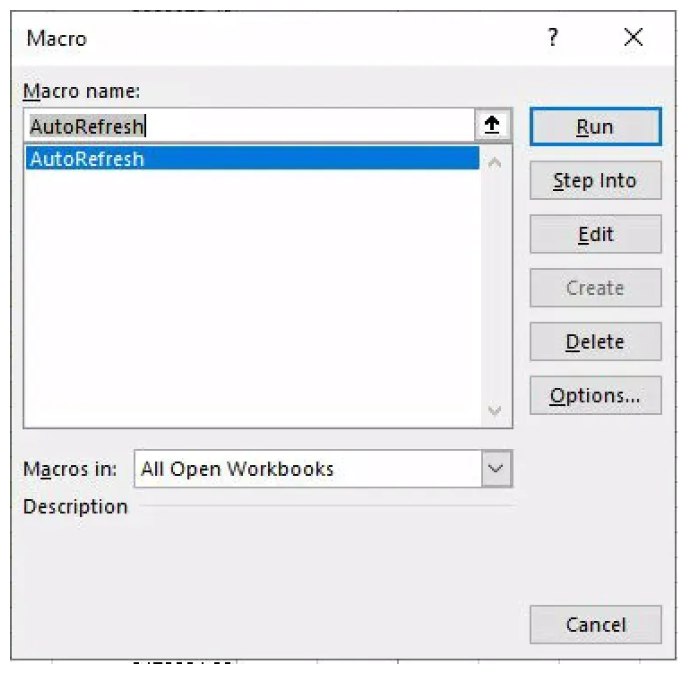 .
.Excel should now start updating your Materialize data at the refresh rate set in the macro.
Best practices
- Index your views: Since Materialize efficiently serves queries from indexed views/indexed materialized views, ensure your views are properly indexed to support frequent refreshes without impacting performance.